An increasing number of companies are adopting the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) to meet ambitious climate goals. Concurrently, EU legislation is advancing with set targets for phasing out combustion engines in the automotive sector and pushing for the adoption of climate-neutral technologies in mobile machinery.
How will these pivotal changes impact construction machines and their supplying industries?
Driving the Transition to Net-Zero
The Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) drives ambitious climate action in the private sector by enabling organizations to set science-based emissions reduction targets. The SBTi is a partnership between CDP, the United Nations Global Compact, World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). The SBTi call to action is one of the commitments of the We Mean Business Coalition, an influential nonprofit organization to take action on climate change.
The implementation of the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) will reshape future construction machinery and therefore have a significant impact on the business of component suppliers.
Globally, companies are embracing decarbonization, setting robust targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in alignment with the Paris Agreement and endorsed by the SBTi. This shift has led to an increased commitment to sustainability goals, including phasing out fossil-fueled vehicles and machinery in favor of electric alternatives.
The number of companies engaged with the SBTi has surged from 116 in 2015 to 4,200 in 2022, reaching 7,000 by the end of 2023. Notably, manufacturers of mobile machinery, including major players like Atlas Copco, CNH, Hitachi, Hyundai, John Deere, Kawasaki, Komatsu, Sandvik, and Volvo, are progressively aligning with the 2030 climate targets.
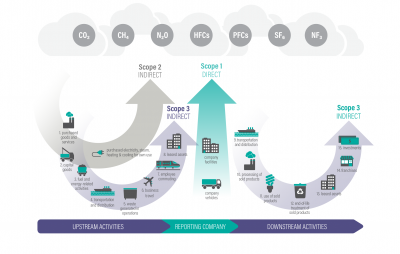
From GHG Protocol’s Technical Guidance for Calculating Scope 3 Emissions, page 6
The implementation of the SBTi will directly and profoundly affect the design and functionality of future construction machinery. This change will significantly alter machine architecture and necessitate adaptations by suppliers in various sectors such as engine technology, hydraulics, and sensor technology. It is essential for OEMs and their suppliers to prepare for these transformative changes.
EU Missions and Urban Initiatives
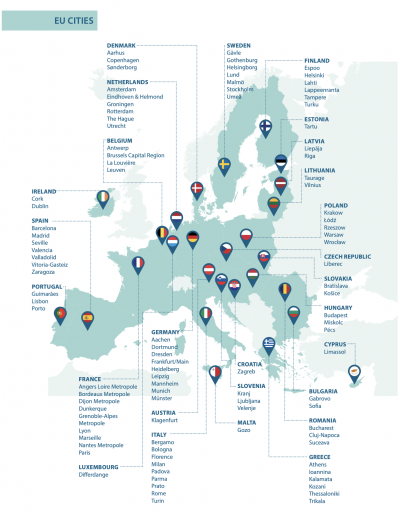
In addition, there are legal and regulatory frameworks for sustainability in the EU evolving: The EU Cities Mission aims to establish 100 climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030, with the broader goal of enabling all European cities to become climate-neutral by 2050. This includes transforming cities like Oslo, Stockholm, and Copenhagen into hubs of experimentation and innovation, focusing on achieving zero-emission construction sites as a key component of their climate strategies.
While the regulatory frameworks for the passenger car and commercial vehicle sectors are well-established, similar regulatory expectations are emerging in the construction machinery sector. These frameworks are crucial in shaping the sustainability goals of companies. OEMs and their suppliers must stay informed and be prepared to adapt to these evolving legal conditions, which are increasingly being enforced by European cities.
Current Innovations in Construction Machines
OEMs have long been at the forefront of adopting new technologies, prominently showcasing their electrified and autonomous solutions during the last years. Diesel engine manufacturers have notably expanded their offerings to include battery-electric drives and hydrogen engines, reflecting a significant industry shift towards cleaner energy sources.
In Spring 2024, this evolution was evident at Intermat in Paris. Companies like Hitachi, Bobcat, and Develon highlighted their forays into autonomous machinery —a crucial adaptation for future construction site operations. Volvo, Liebherr and Mecalac presented their new electric loaders and a variety of electrified excavation and loading equipment.
Further emphasizing the industry's pivot towards sustainable solutions, Zoomlion introduced hybrid concrete mixers, electric aerial work platforms, industrial vehicles with lithium batteries, and energy-efficient technologies for pumps, cranes, and earthmoving equipment. Already earlier in Spring 2024, Sany celebrated the delivery of its 2000th electric loader and launched the SY375E 40t eExcavator, equipped with a battery swap mechanism.
Engine manufacturers like AGCO, Cummins, and Deutz also unveiled new portfolios of environmentally friendly prime movers, signaling a broad-based commitment to emission reduction across the sector.
Below, we present some of the most groundbreacking initiatives.
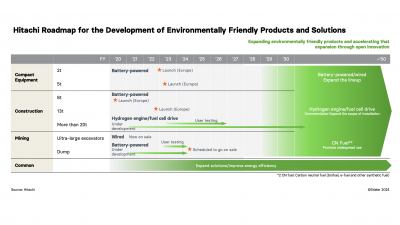
Hitachi Pioneering SBTi Certification
In December 2020, Hitachi set ambitious targets for reducing its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by FY2030. These targets were accredited as "Targets for 1.5℃" by the Science Based Targets initiative.
The specific goals set by Hitachi are:
To reduce absolute scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 100% by 2030, using 2010 as the base year.
To reduce absolute scope 3 GHG emissions by 40% within the same timeframe.
These targets pertain to GHG emissions across various scopes:
Scope 1 and 2 cover direct emissions from owned or controlled sources, including business sites such as factories and offices.
Scope 3 includes indirect emissions from activities in the company’s value chain that are not covered by scopes 1 and 2.
This commitment aligns with the reductions required to keep global warming at 1.5°C, as advocated by the Paris Agreement.
Volvo Battery and Fuel Cell Products at Intermat 2024
Volvo is the most ambitious European player in this field. The company showcased a comprehensive range of new drive solutions in Paris, including the fully electric LH 120H wheel loader, the EC230 excavator, and the ABG P4820 road paver, alongside their HX04 dump truck with a fuel cell system.




Bobcat RogueX2 Autonomous Wheel Loader Concept
The RogueX2 loader, evolved from the RogueX concept unveiled at Conexpo 2023 in Las Vegas, represents an advanced, all-electric and autonomous machine. It features a lithium-ion battery, an electric drive system, and uses electric-actuated lift and tilt kinematics, eliminating traditional hydraulic systems.
This model and its predecessor, RogueX, are designed without a cab to address future workforce shortages by operating without a human operator. By replacing the internal combustion engine with an electric powertrain, the RogueX2 avoids hydraulics, reducing emissions, noise, and environmental risks. It offers enhanced functionality through advanced kinematics that allow multiple types of lift capabilities.
Optimized for electric operation, RogueX2 uses wheels instead of tracks to extend battery life and employs axial flux motors for increased power and efficiency in heavy-duty tasks. These innovations signify a shift towards machines that operate more cleanly and efficiently while eliminating the operator requirement. The concepts have led to many pending patents, emphasizing a transformative approach to machine design and work experience.

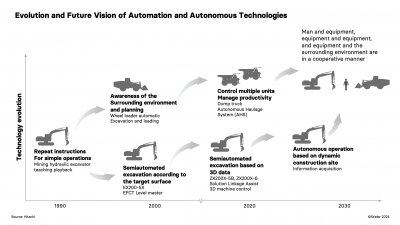
Develon Concept-X 2.0
In 2019, Develon introduced Concept-X, a cutting-edge automated construction solution, in South Korea, and later showcased its upgraded version, Concept-X 2.0, at Intermat. The update features the DD100-CX crawler dozer and the DX225-CX crawler excavator, both designed without cabs and employing a linear core aesthetic.
Key enhancements in Concept-X 2.0 include autonomous driving and blade control using the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), automated 3D grading via a tilt rotator, and enhanced digging and loading operations refined by machine learning algorithms. It also integrates an advanced work planning algorithm and E-Stop safety technology.
Concept-X leverages information and communication technology (ICT) and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate construction tasks, employ drone-based surveying, and utilize unmanned equipment and remote control supported by 5G networks. This aims to boost productivity while minimizing costs and safety risks.
Central to the system is the X-Center, which offers a comprehensive view and control over on-site equipment and operations. It processes terrain data captured by drones to coordinate and manage unmanned equipment effectively. Develon is also developing Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) systems to enable equipment to self-diagnose and predict maintenance needs, thereby enhancing operational reliability and safety.


The Road Ahead
The transition to new main drives is still in its early phases, with manufacturers focusing on replacing traditional diesel engines with alternatives like battery-electric, hydrogen, HVO, and methane systems.
However, simply adopting new main drives will not suffice for future needs. Comprehensive redesigns of the entire machine architecture are necessary to enhance efficiency and meet the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) goals. This comprehensive approach includes:
Selecting appropriate drive solutions.
Implementing more efficient drive functions, including innovations like dual clutches, electric gearboxes, and e-axes.
Enhancing work functions to improve overall machine productivity.
Today’s efficiency goals and technological progress require a redesign of machine architectures. Over time, the growing automation of construction sites will necessitate a shift towards more electric machines.
Hydraulics, a key technology in working machines, must also evolve. To achieve greater efficiency, advanced hydraulic components, such as optimized pumps, motors, and valve solutions, are essential. Machine designers must also explore integrated system solutions.
As technologies advance, electric mechanisms for steering and cooling will become increasingly important in auxiliary drives. The integration of sophisticated chips and software is essential for optimizing these systems, enabling smarter control and integration of machine functions.
In the area of autonomous machinery, the role of advanced sensors, camera systems, processors, and software is expanding, vital for improving machine autonomy and safety. These technologies enable precise navigation, decision-making, and operational efficiency.
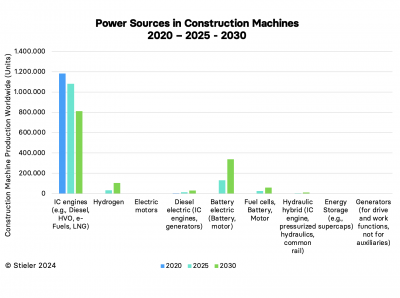
More Diversity in Drive Concepts
In the coming years, we will see more diversity in drive concepts for mobile working machines. This includes a reduction in traditional combustion engines and a rise in diesel-electric hybrids, battery-electric systems, hydrogen-powered engines, and fuel cells.
More about this in our study 'Future Drive Technologies'
Author
How do you navigate this transition?
Find out about our services for OEMs and component suppliers!
Contact us


